Main events:
• After a correction, stocks ended August positively
• Instead of inflation, unemployment results in the USA are now more important
• Revision of GDP growth of the Czech economy from 0.4 to 0.6 in the 2nd quarter of 2024
Summary:
At the beginning of August, there was a smaller approximately 10% correction, which was probably caused by the following factors: an increase in interest rates by the Bank of Japan and simultaneously increased fears of an upcoming economic recession after worse unemployment data.
In the end, however, stocks managed to close positively, and for the month of August, the S&P 500 index gained 2.4%, and even the Japanese Nikkei 225 index, after a drop of up to 15% in one day, ended August in positive numbers. So, is the crisis averted?
It is definitely not possible to say just a month from the time when the probability of a recession in the USA started to increase and when the Fed, in response to worse macroeconomic figures, changed its expectations regarding the reduction of interest rates. Specifically, it is expected that in September there might be a reduction of up to 0.5% and by the end of 2024, the interest rate in the USA could be at 4% from the current 5.5%.
As it has traditionally been in recent years, in September stock indexes experience smaller corrections, and almost from the beginning of September, we see stock indexes slightly declining. Including the Japanese Nikkei 225, which fell by up to 10%.
Regarding macroeconomic data for August, the year-on-year inflation rate in the USA is even below 3%, specifically at 2.9%, and it looks like the Fed has finally got it under control. Unemployment came out a little lower at 4.2%, after July’s increase to 4.3%. So far, it doesn’t look like a deterioration.
The year-on-year inflation rate for July in the Czech Republic came out at 2.2%. GDP growth for the 2nd quarter was revised upwards and grows year-on-year by 0.6% while quarter-on-quarter it grows by 0.3%. However, Germany is stagnating year-on-year for the 2nd quarter and even declines quarter-on-quarter by 0.1%, remaining in recession.
As for the year-on-year inflation results in Europe, it remains at low levels around 2.6% for July, and for August, it is expected to even drop to 2.2. However, the ECB still signals that there will probably not be a significant reduction in interest rates by the end of the year, and we can expect only one or at most two reductions. We will learn all this in the meetings that will take place in September.
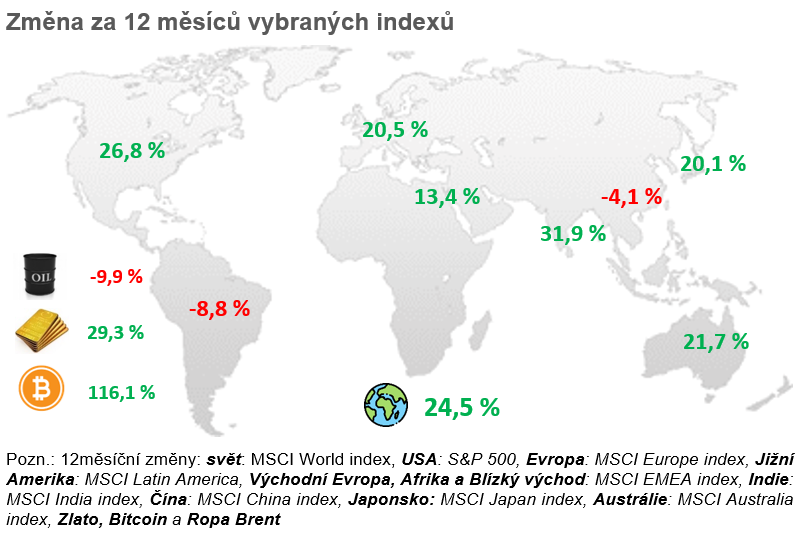
And how did other assets perform? Oil is starting to drop by a few % and we can expect cheaper fuels even here in the Czech Republic. Gold surprisingly reached new highs again, currently at over USD 2560 per troy ounce. Bitcoin, within the August correction, fell even below USD 50,000. However, it then grew again and is currently holding at around USD 55,000.
CZ:
The year-on-year inflation rate for July remains within the tolerance range and came out at 2.2%. Inflation is no longer the main topic within the Czech Republic.
A more important topic is the level of GDP growth, which after the revision brought quite a positive result for the 2nd quarter of 2024. GDP was revised upwards and grows year-on-year by 0.6% while quarter-on-quarter it grows by 0.3%.
Year-on-year GDP growth in the Czech Republic
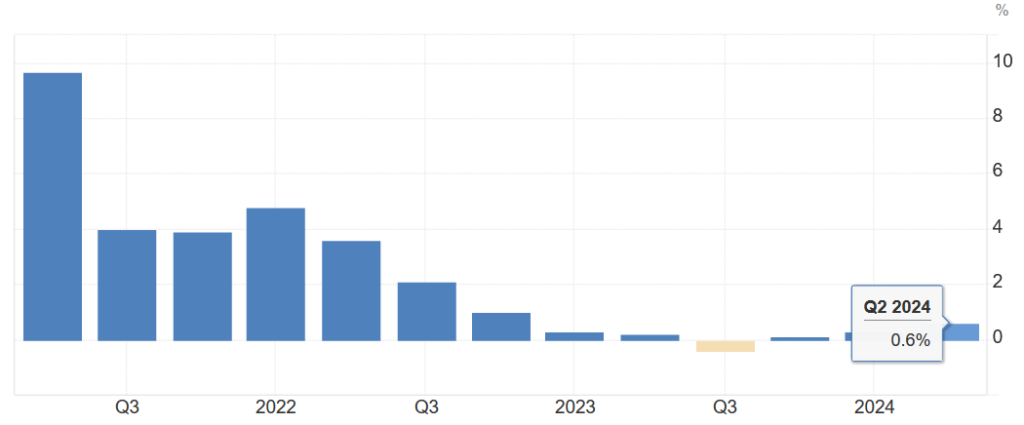
Source: tradingeconomics.com
As of 1.9. 2024, a law that charges for early mortgage repayment came into effect. Until now, early repayment was free or for only a minimal fee, but from September we will pay up to 0.25% of the early repaid amount for each started year remaining until the end of the interest rate fixation, but no more than 1% of the early repaid amount.
The new rules apply to credit agreements concluded after September 1, 2024. For ongoing contracts, the rules apply only to clients who repay their mortgage early during a fixation that will be agreed upon after September 1, 2024.
USA:
Inflation in the USA confirms a definitely declining trend, and the year-on-year rate for July came out at 2.9%. Services and real estate prices no longer drive growth, and it really looks like inflation in the USA no longer needs to worry the Fed or stock markets.
The next Fed meeting awaits us in September, and it is currently expected that for the first time in several years there might be a reduction. Possibly even by 0.5%.
Market expectations regarding interest rate reductions
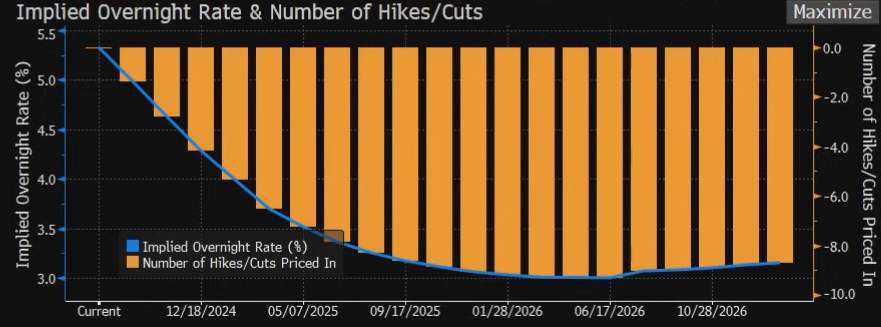
Source: Bloomberg
At the same time, it is expected that by the end of the year the interest rate in the USA could be only at 4%, and in 2025 it should then be reduced almost to 3%.
Instead of inflation, more interesting and watched numbers regarding unemployment, which could signal a possible recession, are currently being discussed. Unemployment came out a little lower in August at 4.2%, after July’s increase to 4.3%. So far, it doesn’t look like a deterioration, but it was expected to create new jobs up to 164 thousand, and instead, only 142 thousand were created.
In the previous commentary, we described the inverted yield curve and what historically happened after it occurred. Specifically, in 100% of cases, a recession occurred within a year or two. However, usually only after the inverted curve straightened again (the difference was positive) and short-term bonds yielded lower returns than long-term ones.
Therefore, I provide an update, where at the beginning of September, interest rates on both short-term and long-term government bonds in the USA were declining.
Yield difference between 2 and 10-year US bonds
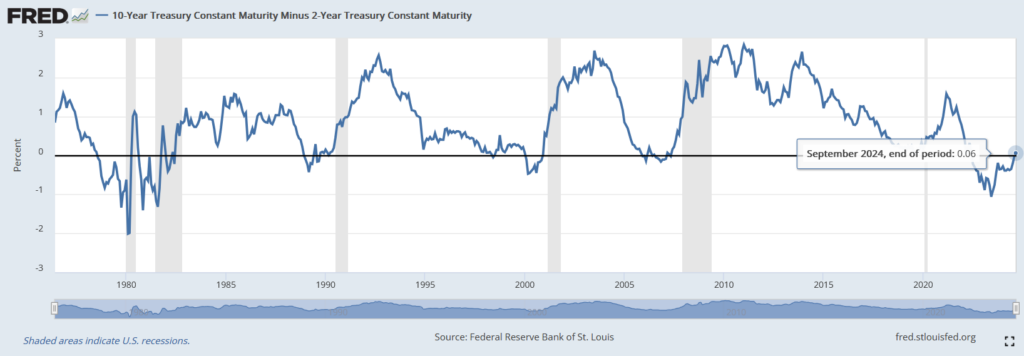
Source: Fred.com
Until recently, we had an inverted yield curve, but today we are already in a state where the inverted curve has straightened, and the short-term yield is thus lower than the yield on long-term government bonds. Which is a normal state for the economy and financial markets.
The S&P 500 index gained 2.4% in August, NASDAQ 100 gained 1.14%. However, both indexes are declining since the beginning of September.
Europe:
The year-on-year inflation rate for July in Europe remains at the expected 2.6%, and inflation figures again confirm that the episode of high inflation is over. For August, a drop in inflation to just 2.2% is even expected.
The ECB meeting awaits us in September, and it is not yet clear how quickly the ECB will continue to lower interest rates.
Year-on-year GDP growth in Germany
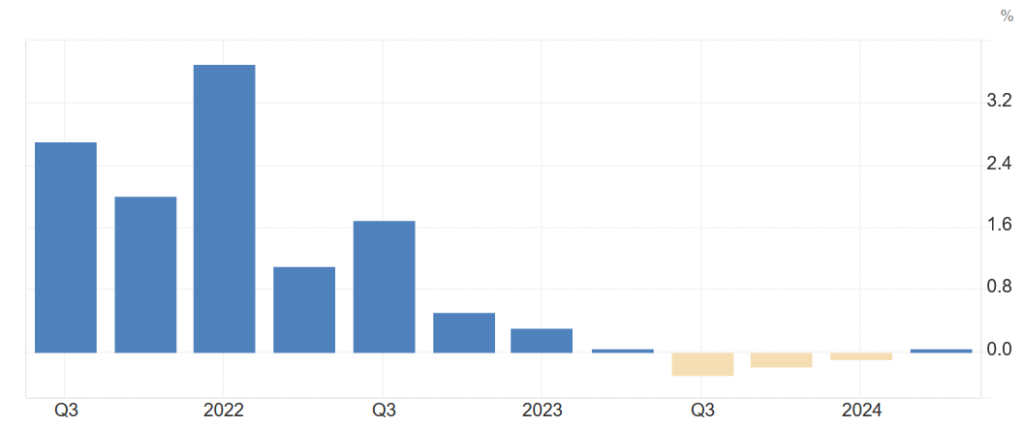
Source: tradingeconomics.com
However, Germany is deepening its recession, and for the 2nd quarter of 2024, it even falls quarter-on-quarter by 0.1%. Year-on-year, it is stagnation at 0%. They are still unable to kickstart the economy, and reports from large car manufacturers like Volkswagen, which wants to lay off even more and limit its production in Germany, do not help.
The European MSCI Europe index grew by even 3.95% in August.
